Why is Occlusion in Augmented Reality So Hard?
 The main problem with all the above systems is that in terms of depth sensing, they have:
The main problem with all the above systems is that in terms of depth sensing, they have:
- Poor range (<4m): The size and power limitations of mobile devices restrict the range of IR and Stereo depth sensors.
- Low resolution: Smaller objects in the scene are not discernible in the point cloud and it’s really hard to achieve crisp and reliable occlusion surfaces.
- Slow mesh reconstruction: Current methods of generating meshes from point clouds are too slow for real-time occlusion on these devices.
How can you hack occlusion today ?
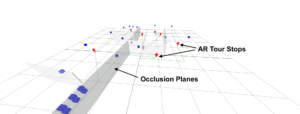
Perfect occlusion is an elusive target, but we can get close to it in some situations, especially when we can relax the real-time constraint.
If the application allows pre-mapping the environment, it’s possible to use a pre-built mesh as an occlusion mask for the larger prominent objects in the scene, provided they don’t move.
This means that you’re not limited to the 4m range of the depth sensor, at least for occlusion behind static objects.
Moving objects are still a problem and the only solution right now it to use the depth map masking method for close range moving objects like your hands.
In fact, centimeter-level position tracking indoors and outdoors is a critical component of occlusion and through our work with Placenote, we’re working towards a cloud-based visual positioning system that can solve some of these problems.
See the full, long article here: https://hackernoon.com/why-is-occlusion-in-augmented-reality-so-hard-7bc8041607f9
Pages
- About Philip Lelyveld
- Mark and Addie Lelyveld Biographies
- Presentations and articles
- Tufts Alumni Bio