Meet the next generation of AI superstars
... Sharon Li, pictured above and our Innovator of the Year, is an assistant professor at the University of Wisconsin, Madison. She created a remarkable AI safety feature called out-of-distribution detection. This feature helps AI models determine if they should abstain from action when faced with something they weren’t trained on. This is crucial as AI systems are rolled out from the lab and encounter new situations in the messy real world. ...
Richard Zhang, a senior research scientist at Adobe, invented the visual similarity algorithms underlying image-generating AI models like Stable Diffusion and StyleGAN. Without his work, we would not have the image-generating AI that has captivated the world. ...
Read the full list of 35 under 35 here: https://www.technologyreview.com/innovators-under-35/2023/?truid=&utm_source=the_algorithm&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=the_algorithm.unpaid.engagement&utm_content=09-18-2023
See the full story here: https://www.technologyreview.com/2023/09/19/1079846/meet-the-next-generation-of-ai-superstars/
Is that a model, or AI?
...
If AI, augmented reality and 3D-rendering tools are used responsibly, some image-makers believe they’ll boost creativity. “I haven’t been this positive and this excited since the beginning of the internet,” said Nick Knight, an experimental photographer in London who has worked with Alexander McQueen and Givenchy. “Fashion, which is about change and newness, should really be embracing this,” he said. During the pandemic Knight had Kendall Jenner photograph herself “thousands of times,” so he could create an avatar from her likeness. That avatar walked in a virtual runway show for Burberry.
“Creators and models alike will need to adapt and learn how to license their likeness and make a living from their art in new ways,” said Lyle Stevens, co-founder of Boston influencer-marketing company Mavrck. His company is experimenting with creating AI influencers and launched the Instagram account @Beyondbowwow, which features realistic AI-generated dogs and people.
See the full story here: https://www.wsj.com/style/fashion/ai-models-levis-nars-influencers-8cab8ba5

Nvidia, Palantir and more companies join White House AI pledge
... Fifteen of the most influential companies in the United States have now taken the commitments, which include a promise to develop technology to identify AI-generated images and a vow to share data about safety with the government and academics.
New participants include IBM, data-mining company Palantir and Stability, the maker of text-to-image generator Stable Diffusion, underscoring the expansion of the pledge beyond AI heavyweights such as Microsoft and Meta and OpenAI, the maker of ChatGPT. ...
“The President has been clear: harness the benefits of AI, manage the risks, and move fast — very fast,” Zients said in a statement. “And we are doing just that by partnering with the private sector and pulling every lever we have to get this done.”
The commitments will apply to the next system released by each of the companies, the administration official said. ...
See the full story here: https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2023/09/12/white-house-ai-ibm-nvidia-pledge/
Deloitte: Consumer Views of Connected Devices Are Changing
“More than 6 in 10 Gen Z respondents and over half of millennials expressed interest in learning, socializing and shopping through 3D platforms.” ...
Smart home devices have become indispensable and are often being used to help increase home security, according to Deloitte Vice Chair and U.S. Technology Sector Leader Paul Silverglate, who points out that:
- Among consumers surveyed, 34 percent were victim to at least one kind of security breach in the past year, and 16 percent experienced two or more.
- Gen Zs were more than twice as likely as boomers to have their social media account hacked (17 percent vs. 8 percent) and three times more likely than baby boomers to fall for an online scam (16 percent vs. 5 percent).
- Smart home devices that most owners consider essential all relate to home safety, including smart door locks, smart smoke detectors, security systems and doorbells with cameras.
See the full story here: https://www.etcentric.org/deloitte-consumer-views-of-connected-devices-are-changing/
Our quick guide to the 6 ways we can regulate AI
A legally binding AI treaty
The OECD AI principles
The Global Partnership on AI
The EU’s AI Act
Technical industry standards
The United Nations
The United Nations, which counts 193 countries as its members, wants to be the sort of international organization that could support and facilitate global coordination on AI. In order to do that, the UN set up a new technology envoy in 2021. That year, the UN agency UNESCO and member countries also adopted a voluntary AI ethics framework, in which member countries pledge to, for example, introduce ethical impact assessments for AI, assess the environmental impact of AI, and ensure that AI promotes gender equality and is not used for mass surveillance.
Pros: The UN is the only meaningful place on the international stage where countries in the Global South have been able to influence AI policy. While the West has committed to OECD principles, the UNESCO AI ethics framework has been hugely influential in developing countries, which are newer to AI ethics. Notably, China and Russia, which have largely been excluded from Western AI ethics debates, have also signed the principles.
Cons: That raises the question of how sincere countries are in following the voluntary ethical guidelines, as many countries, including China and Russia, have used AI to surveil people. The UN also has a patchy track record when it comes to tech. The organization’s first attempt at global tech coordination was a fiasco: the diplomat chosen as technology envoy was suspended after just five days following a harassment scandal. And the UN’s attempts to come up with rules for lethal autonomous drones (also known as killer robots) haven’t made any progress for years.
Influence rating: 2/5
See the full story here: https://www.technologyreview.com/2023/05/22/1073482/our-quick-guide-to-the-6-ways-we-can-regulate-ai/
A Race to Extinction: How Great Power Competition Is Making Artificial Intelligence Existentially Dangerous
...
Beyond the world of text, generative applications Midjourney, DALL-E, and Stable Diffusion produceunprecedentedly realistic images and videos. These models have burst into the public consciousness rapidly. Most people have begun to understand that generative AI is an unparalleled innovation, a type of machine that possesses capacities — natural language generation and artistic production — long thought to be sacrosanct domains of human ability.
But generative AI is only the beginning. A team of Microsoft AI scientists recently released a paperarguing that GPT-4 — arguably the most sophisticated LLM yet — is showing the “sparks” of artificial general intelligence (AGI), an AI that is as smart — or smarter — than humans in every area of intelligence, rather than simply in one task. They argue that, “[b]eyond its mastery of language, GPT-4 can solve novel and difficult tasks that span mathematics, coding, vision, medicine, law, psychology and more, without needing any special prompting." In these multiple areas of intelligence, GPT-4 is “strikingly close to human-level performance.” In short, GPT-4 appears to presage a program that can think and reason like a human. Half of surveyed AI experts expect an AGI in the next 40 years. ...
The pressure to outpace adversaries by rapidly pushing the frontiers of a technology that we still do not fully understand or fully control — without commensurate efforts to make AI safe for humans — may well present an existential risk to humanity’s continued existence. ...
...just the perception of falling behind an adversary contributed to a destabilizing buildup of nuclear and ballistic missile capabilities, with all its associated dangers of accidents, miscalculations, and escalation. ...
The Alignment Problem
Despite dramatic successes in AI, humans still cannot reliably predict or control its outputs and actions. While research focused on AI capabilities has produced stunning advancements, the same cannot be said for research in the field of AI alignment, which aims to ensure AI systems can be controlled by their designers and made to act in a way that is compatible with humanity’s interests. ...
Arms Racing or Alignment Governance? A Risky Tradeoff
How does international competition come into play when discussing the technical issue of alignment? Put simply, the faster AI advances, the less time we will have to learn how to align it. ...
Likewise, the perception of an arms race may preclude the development of a global governance framework on AI. A vicious cycle may emerge where an arms race prevents international agreements, which increases paranoia and accelerates that same arms race. ...
However, the outlook is not all rosy: as the political salience of AI continues to increase, the questions of speed, regulation, and cooperation may become politicized into the larger American partisan debate over China. Regulation may be harder to push when “China hawks” begin to associate slowing AI with losing an arms race to China. Recent rhetoric in Congress has emphasized the AI arms race and downplayed the necessity of regulation. ...
See the full story here: https://hir.harvard.edu/a-race-to-extinction-how-great-power-competition-is-making-artificial-intelligence-existentially-dangerous/
TIME Reveals Inaugural TIME100 AI List of the World’s Most Influential People in Artificial Intelligence
See the list here: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/time-reveals-inaugural-time100-ai-list-of-the-worlds-most-influential-people-in-artificial-intelligence-301920536.html
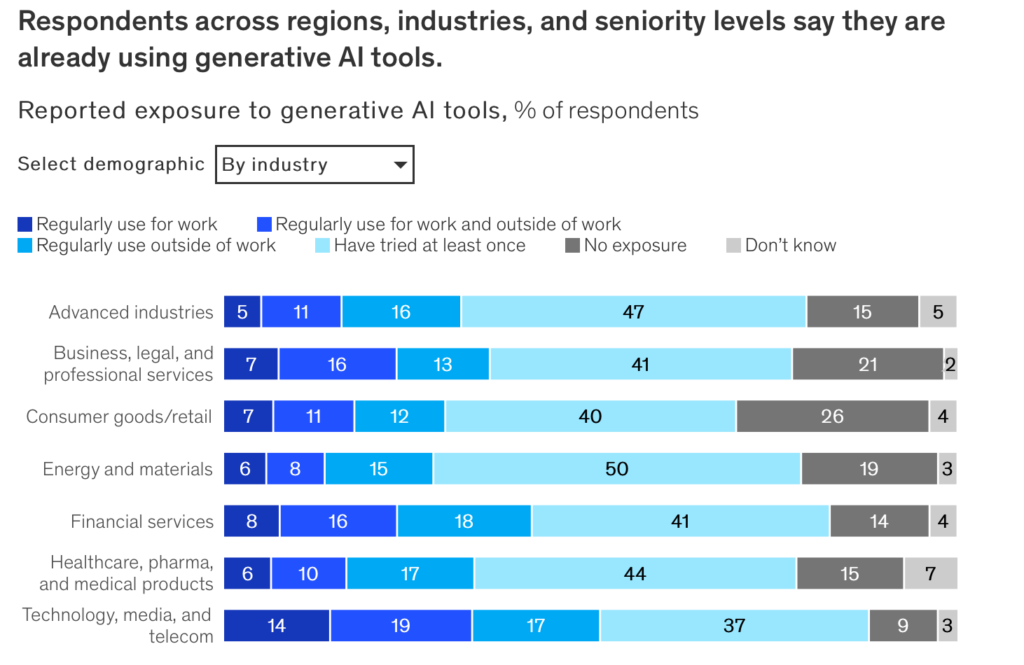
[McKinsey] What’s the future of generative AI? An early view in 15 charts
See the full story with 15 charts here: https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/mckinsey-explainers/whats-the-future-of-generative-ai-an-early-view-in-15-charts?cid=other-eml-shl-mip-mck&hlkid=4a4d7c3a72aa49968c53834a9cccf217&hctky=2717270&hdpid=4a4b61b4-1426-42b1-aa20-8e6948de518d
The Role of Reputation Systems Within Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) have become an increasingly popular way to organize groups and projects in a decentralized manner through blockchain technology. DAOs allow people to collaborate and make decisions collectively without centralized control. However, ensuring accountability within decentralized structures presents unique challenges. This is where reputation systems come in.
Reputation systems help build trust and alignment among members of a decentralized community. Within a DAO, reputation systems allow members to rate each other based on contributions, character, and reliability. High reputation scores act as a signal of status and trustworthiness. In a space where anonymity and pseudonymity are common, reputation systems create transparency around identity and track record. As DAOs continue to gain adoption, well-designed reputation systems will be key to their success. ...
Members are incentivized to contribute value and act honestly to garner high reputation scores. Concurrently, high reputation members signal that they are trustworthy allies. ...
Mentorship programs matching high reputation members with newcomers also foster inclusive onboarding. Temporary reputation boosts for being vouched by existing members is another onboarding design. The goal is healthy socialization and information osmosis. ...
See the full story here: https://btcpeers.com/the-role-of-reputation-systems-within-decentralized-autonomous-organizations/
Google to require disclosure for AI in election ads
...
Why it matters: The explosion of generative AI has raised questions over its use to create deceptive content in an online political environment already rife with misinformation.
- Online election ads remains a fairly unregulated space, though the FEC is mulling expanded new rules, as Axios previously reported. ...
Details: Language on the disclosures may say things like "this audio was computer generated" or "this video content was synthetically generated," per the announcement. ...
- The policy will be enforced using a combination of human review and tech tools to examine ads, and ads will be disapproved or removed accordingly. Advertiser accounts that engage in pervasive or egregious violations may be suspended, Aciman said.
- Advertisers will be notified if an ad is rejected and will have the ability to appeal and re-upload with the proper disclosure.
See the full story here: https://www.axios.com/2023/09/06/google-ai-election-ads-disclosure
Pages
- About Philip Lelyveld
- Mark and Addie Lelyveld Biographies
- Presentations and articles
- Tufts Alumni Bio